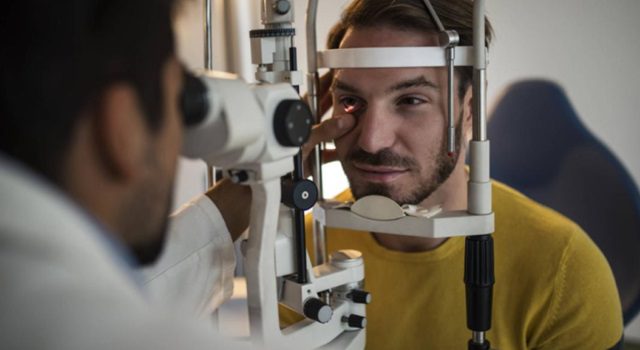
BTN News: Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly. It occurs when the retina, a crucial layer of tissue at the back of the eye, separates from its supporting tissues. This detachment cuts off the retina’s blood supply, leading to blurred vision and, if untreated, potentially permanent blindness. An immediate consultation with an ophthalmologist is vital to address this condition before irreversible damage occurs.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Retinal Detachment
A sudden onset of vision changes could signal a retinal detachment. Look out for the following symptoms:
- Floaters: Small black spots or “floaters” that seem to drift across your vision.
- Flashes of Light: Unexpected flashes or bursts of light, especially in peripheral vision.
- Wavy or Distorted Vision: A sudden distortion, making straight lines appear bent or wavy.
- Dark Shadows: A curtain-like shadow that gradually covers part of your vision.
- Blurred Vision: General blurriness that doesn’t improve with glasses or rest.
- Rapid Vision Loss: A quick decrease in vision clarity, sometimes leading to total blindness in the affected eye.
These symptoms can develop suddenly, making it crucial to seek medical help immediately to prevent permanent damage.
What Causes Retinal Detachment? Key Risk Factors Explained
Retinal detachment can occur due to a variety of reasons, and understanding the causes is key to prevention. The most common causes include:
- Age-Related Changes: As we age, the vitreous, the gel-like substance inside the eye, can shrink and pull away from the retina.
- Eye Injuries or Inflammation: Previous trauma or inflammation can weaken the retina’s attachment.
- High Myopia (Nearsightedness): People with severe nearsightedness have a thinner retina, increasing the risk of detachment.
- Previous Eye Surgeries: Such as cataract removal, which can alter the structure of the eye.
Other risk factors can include family history, certain genetic conditions, and previous instances of retinal detachment.
Understanding the Different Types of Retinal Detachment
There are three main types of retinal detachment, each with unique characteristics:
- Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment: This is the most common type, caused by a tear or break in the retina that allows fluid to seep underneath, separating it from the underlying tissue.
- Tractional Retinal Detachment: Often found in people with diabetes, this type occurs when scar tissue on the retina’s surface contracts, pulling the retina away from the back of the eye.
- Exudative Retinal Detachment: This type is due to fluid accumulating beneath the retina without a tear or break, often linked to inflammatory disorders or eye injuries.
Critical Treatment Options: From Surgery to Recovery
Treating retinal detachment typically involves surgery, and the choice of procedure depends on the severity and type of detachment:
- Scleral Buckling Surgery: A silicone band is placed around the eye to push the wall of the eye against the detached retina.
- Vitrectomy: The removal of the vitreous gel and replacing it with a gas bubble or oil to reattach the retina.
- Pneumatic Retinopexy: A gas bubble is injected into the eye to press the retina back into place.
These procedures are crucial to restore vision and prevent further damage. Prompt surgical intervention is often needed to ensure the best outcome.
Prevention and Early Detection: Key to Preserving Vision
While not all retinal detachments are preventable, being aware of risk factors and symptoms is vital. Regular eye check-ups, especially for those with high myopia or a family history of retinal issues, can help detect early signs and prevent severe outcomes. Immediate medical attention at the first sign of symptoms, such as new floaters or flashes of light, is essential to prevent vision loss.
Take Action: Visit an Ophthalmologist at the First Sign of Symptoms
If you experience any signs of retinal detachment, do not delay. Seek an ophthalmologist immediately for an evaluation. Treatment is most effective when the detachment is detected early. In places like the Barcelona Eye Care Center, specialized teams are available to provide prompt and effective treatment, potentially saving your sight.
Conclusion: Be Proactive About Your Eye Health
Retinal detachment is a medical emergency that can lead to permanent vision loss if untreated. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your eyesight. Remember, early detection and immediate intervention by an eye care professional can make all the difference.