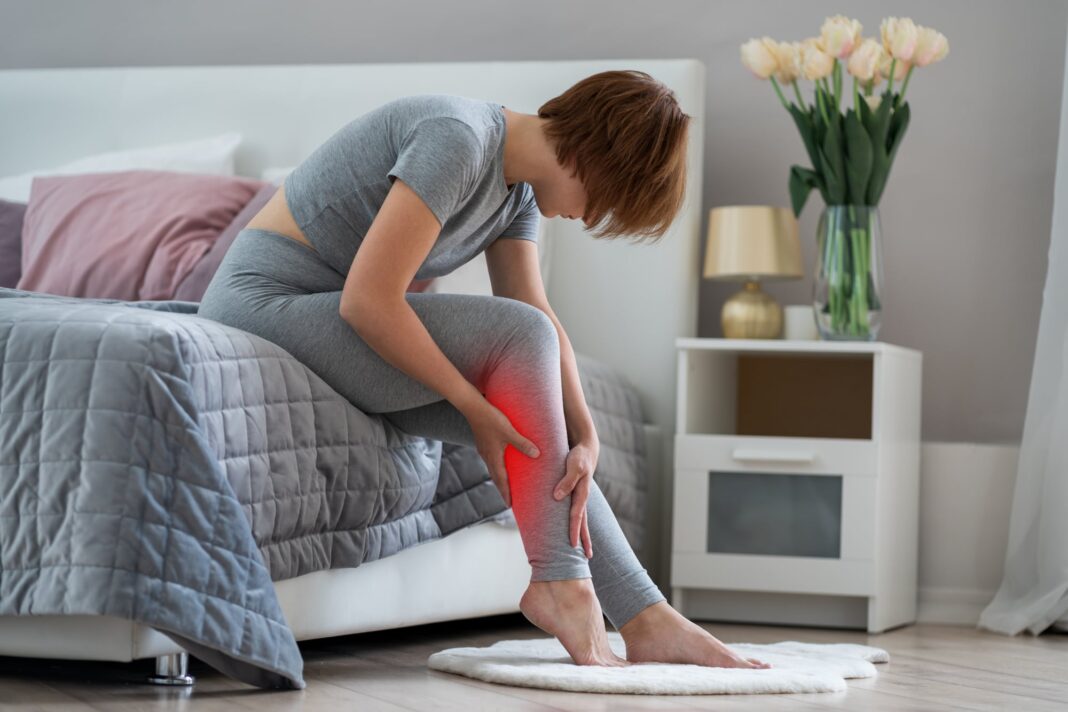
BTN News: Muscle cramps can strike anyone, but they are especially common during the night. These painful spasms, often affecting the legs, disrupt sleep and cause discomfort. For years, many have turned to a popular remedy—drinking tonic water before bed—to prevent these nighttime leg cramps. The reasoning? Tonic water contains quinine, a compound once used to treat muscle pain. However, recent findings from Harvard Health Publishing challenge the effectiveness of this remedy, suggesting instead that proper hydration and stretching exercises may be more reliable solutions. If you’re struggling with muscle cramps, read on to learn what really works, according to the latest research.
The Truth About Tonic Water and Quinine
For decades, the advice to drink tonic water before bedtime has circulated as a go-to remedy for preventing leg cramps. This suggestion stems from the fact that tonic water contains quinine, a compound historically used for treating certain types of muscle pain and malaria. Yet, Harvard experts have now debunked this common belief. According to an article published in Harvard Health Publishing, there is no strong scientific evidence supporting the use of tonic water—or its quinine content—for preventing muscle cramps.
Why Quinine Isn’t the Answer
Despite its medicinal history, quinine is not recommended for treating muscle cramps. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has only approved quinine for malaria treatment due to its potential side effects, such as irregular heart rhythms and even bleeding complications. Moreover, the quinine content in tonic water is far below the therapeutic dose needed to be effective against cramps. So, while consuming tonic water isn’t necessarily harmful, it is unlikely to provide significant relief from nighttime leg cramps.
Effective Alternatives: Staying Hydrated and Active
If tonic water isn’t the answer, what can help prevent those painful nocturnal spasms? Experts from both Harvard and the Mayo Clinic emphasize the importance of proper hydration. Hydration is key—muscles need to stay hydrated to function correctly. Dehydration is one of the main culprits behind muscle cramps. Drinking enough water throughout the day, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing cramps at night.
The Role of Alcohol and Caffeine
To further support hydration, it’s advisable to limit or avoid alcohol and caffeine intake. Both substances can dehydrate the body, increasing the likelihood of cramps. Staying mindful of your fluid intake and making these small adjustments can make a significant difference.
Pre-Bedtime Stretching: A Simple, Proven Solution
Another effective strategy is incorporating light stretching exercises before going to bed. Activities such as stretching the calf muscles or using a stationary bike for a few minutes can help keep muscles relaxed throughout the night. Regularly stretching the legs, especially the calves, has been shown to reduce the frequency and intensity of muscle cramps.
Why Are Nighttime Cramps So Common in Older Adults?
While anyone can experience muscle cramps, they tend to be more frequent in older adults. Aging muscles lose some of their flexibility and may become more prone to cramping due to decreased circulation or deficiencies in key minerals. However, that doesn’t mean younger people are immune. Those who are physically active or have mineral deficiencies, such as low levels of potassium, magnesium, or calcium, may also suffer from these painful spasms.
Final Thoughts: What Works Best for You?
While drinking tonic water before bed might not be the effective cure it was once thought to be, there are proven ways to reduce the risk of nighttime leg cramps. Staying well-hydrated, avoiding dehydrating substances like alcohol and caffeine, and incorporating simple stretching exercises into your routine can help keep those cramps at bay. As always, consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best prevention strategies for your specific situation.